Conditions Of The Heart
It is a life-threatening condition where the heart suddenly can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. It’s most commonly caused by a severe heart attack, but not everyone who has a heart attack develops cardiogenic shock.
The circulatory System
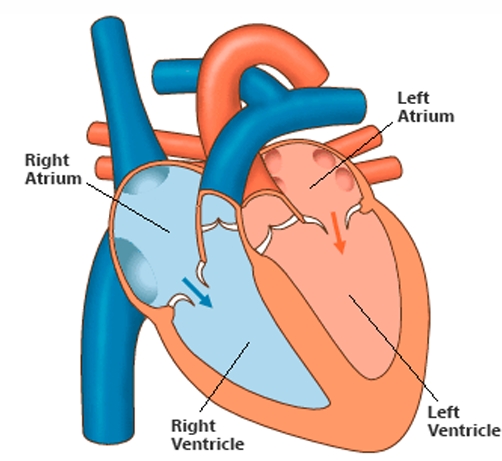
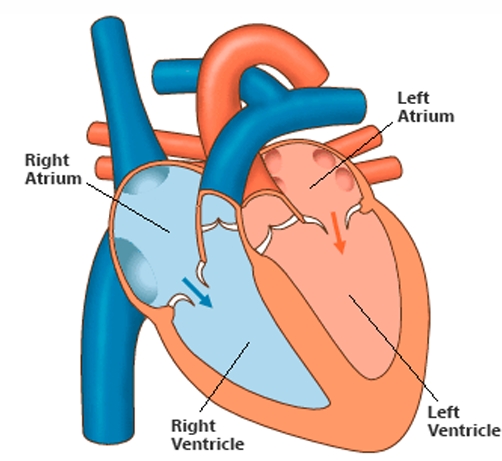
The heart is divided into four chambers, each playing a vital role in pumping blood throughout the body:
- Right Atrium: Receives oxygen-poor blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava. It then sends the blood to the right ventricle.
- Right Ventricle: Pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery, where it picks up oxygen.
- Left Atrium: Receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins and passes it to the left ventricle.
- Left Ventricle: The strongest chamber, it pumps oxygen-rich blood to the entire body through the aorta.
Each chamber works in harmony to keep circulation flowing efficiently.
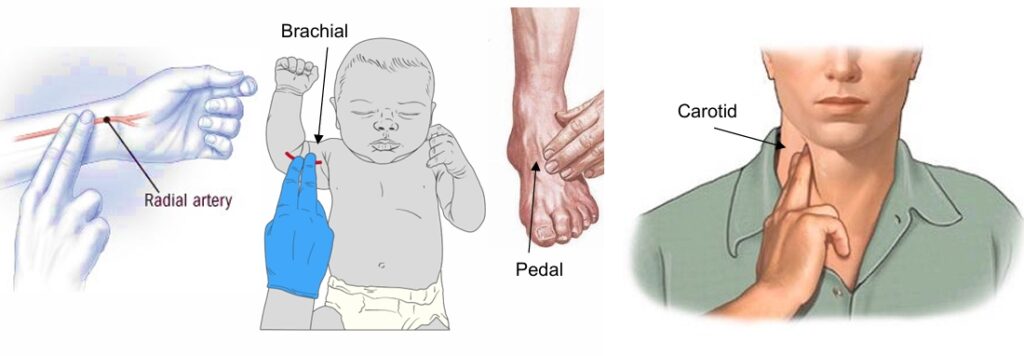
Checking The Pulse
Checking your pulse is a simple way to measure your heart rate. You can find your pulse in several places, but the most common are:
- Wrist (Radial Pulse): Place your index and middle fingers on the inside of your wrist, just below the base of your thumb. Press lightly until you feel the pulse.
- Neck (Carotid Pulse): Place your fingers on the side of your neck, just below your jawline, and press gently until you feel the pulse.
- Foot (Pedal Pulse): You can also check your pulse on the top of your foot by placing your fingers above the highest point of the bone that runs along the top.
- Elbow (Brachial Pulse): This method is commonly used for young children. Place your fingers on the inside of the arm, between the crook of the elbow and the pointy part of the elbow bone.
Once you find your pulse, count the beats for 30 seconds and multiply by 2 to get your heart rate in beats per minute (bpm). A normal resting heart rate is typically between 60 and 100 bpm. If your pulse feels irregular or unusually fast or slow, it might be worth checking with a doctor.
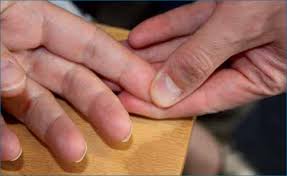
Capillary refill
Is a quick test used to assess blood circulation in the body’s extremities. Press on a fingernail or skin until it turns pale, then release the pressure and observe how long it takes for the color to return. Normally, this should happen within 2 seconds. A delayed refill time can indicate conditions like dehydration, shock, or poor blood flow.
Watch the short clip that explains the function of the human heart
Angina

Angina is a condition that causes chest pain or discomfort due to reduced blood flow to the heart. It can feel like pressure, tightness, or squeezing in the chest and may also be felt in the arms, neck, jaw, back, or stomach.
There are different types of angina, including:
- Stable angina: Occurs during physical exertion or stress and usually improves with rest or medication.
- Unstable angina: More unpredictable and can happen even at rest, requiring urgent medical attention.
- Vasospastic angina: Caused by spasms in the coronary arteries.
- Microvascular angina: Involves small blood vessels in the heart.
If you experience chest pain that does not go away with rest or medication, it could be a sign of a heart attack, and you should seek emergency medical help immediately.
Angina Treatment
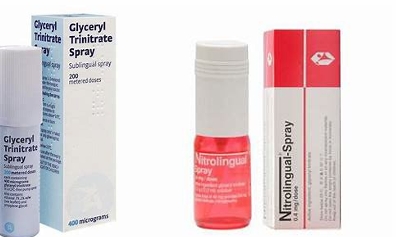
Glyceryl Trinitrate (GTN): A medication used to treat angina (chest pain) and anal fissures. It works by relaxing blood vessels to improve blood flow.

- Sit the casualty on the floor.
- Call 999/112
- Allow them to take their own medication if available
- Be prepared for resuscitation, the condition can deteriorate quickly
- Get an AED if nearby or send someone to get it.
Heart Attack
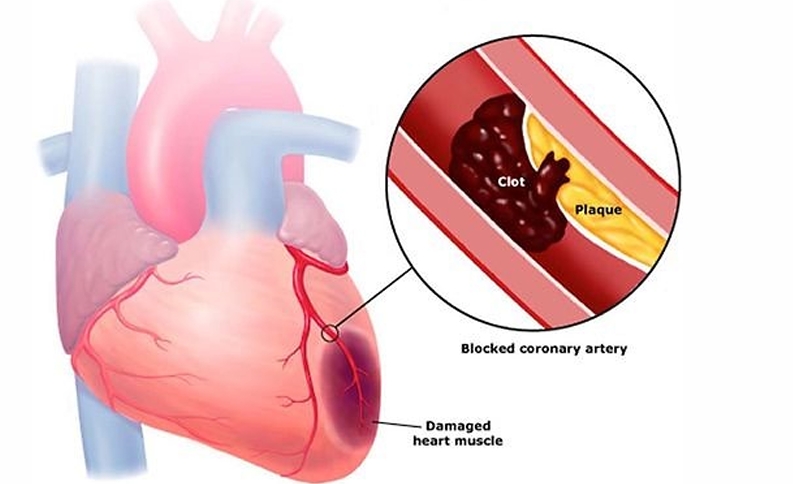
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is suddenly blocked, usually by a blood clot. This can cause serious damage to the heart muscle and is a medical emergency.
Common Symptoms:
Dizziness or nausea – feeling lightheaded or sick.
Chest pain – pressure, tightness, or squeezing across the chest.
Pain in other areas – arms (especially the left), jaw, neck, back, or stomach.
Shortness of breath – even without exertion.
Sweating – sudden cold sweats.
Treatment
heart attack is a medical emergency, and immediate treatment is crucial. If you suspect someone is having a heart attack, call emergency services (999 /112 immediately.
While waiting for medical help, here are some steps that may help:
- Stay calm and sit down to reduce strain on the heart.
- Chew and swallow a 300mg aspirin (if not allergic) to help thin the blood.
- Avoid unnecessary movement to prevent further stress on the heart.
- Get AED and be prepared for CPR
Left Ventricular Failure
Left ventricular failure is a type of heart failure where the left side of the heart struggles to pump blood effectively. This can lead to symptoms like shortness of breath, persistent coughing, fatigue, and swelling in the legs or abdomen, pale sweaty skin. Fluids back up into the airways, frothy sputum which may contain blood is coughed up making breathing very difficult
Common causes include coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, heart attacks, and certain heart rhythm disorders. Treatment often involves medications, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgical interventions
Treatment
LVF is a medical emergency, and immediate treatment is crucial. , call emergency services (999 /112 immediately. Keep casualty sat up to help with breathing. Allow them to use medication if available.
On the next page, we will look at Anaphylaxis shock and Airway/breathing problems.